
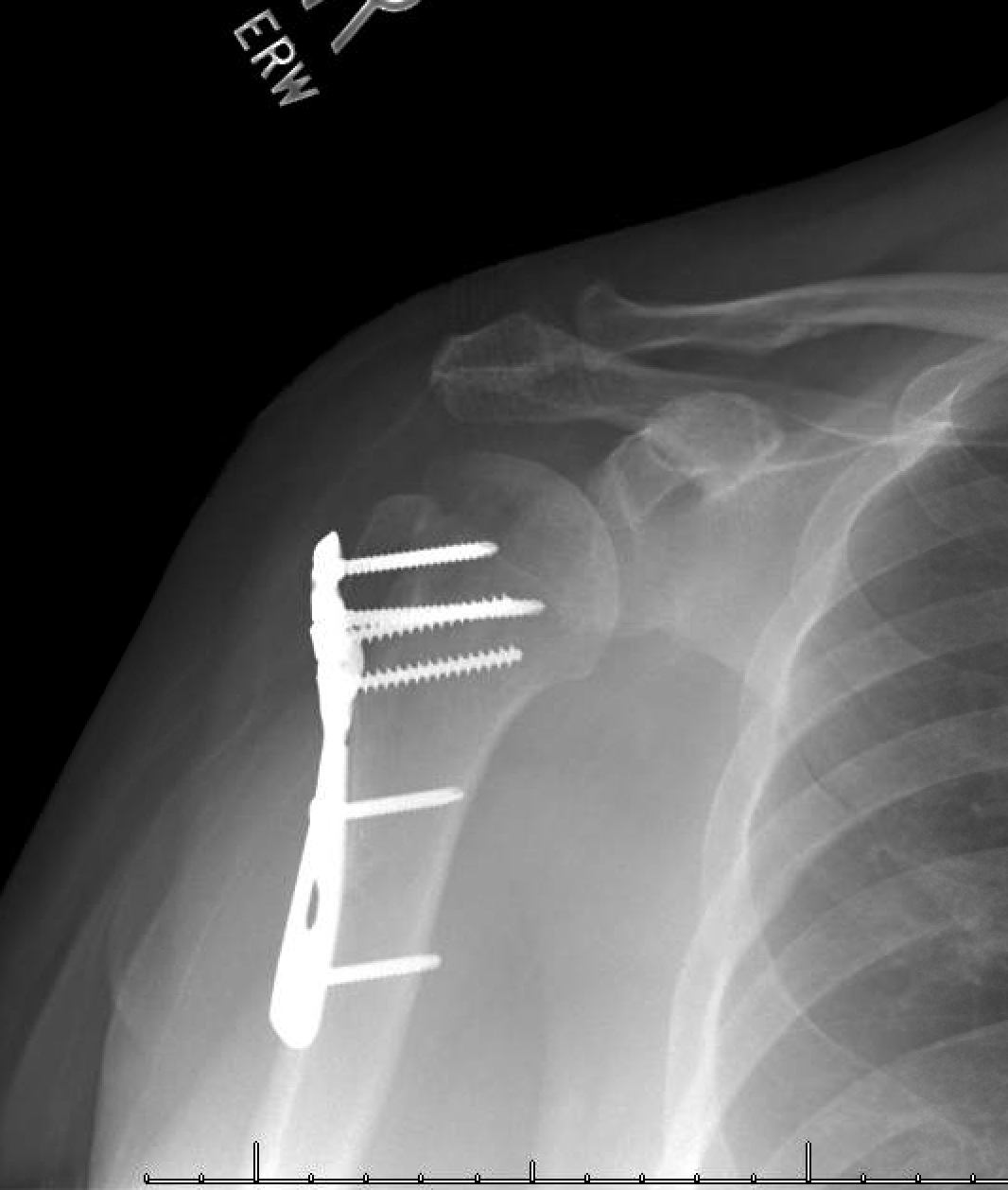
Case Report IĪ 92-year-old woman was referred to the emergency room after she was found at home lying for approximately 2.5 hours at the floor after a fall on her left shoulder. Furthermore, we wanted to show that endovascular procedures are valuable alternatives to open procedures with a minimum of additional trauma. In second place by the fact that there is a considerable variation in clinical symptoms of these fractures. This paper was motivated in the first place by the rareness and severity of vascular complications accompanying a proximal humeral fracture. In this paper, we present two cases of closed proximal humeral fractures with accompanying vascular lesions due to fracture displacement and describe the treatment options.
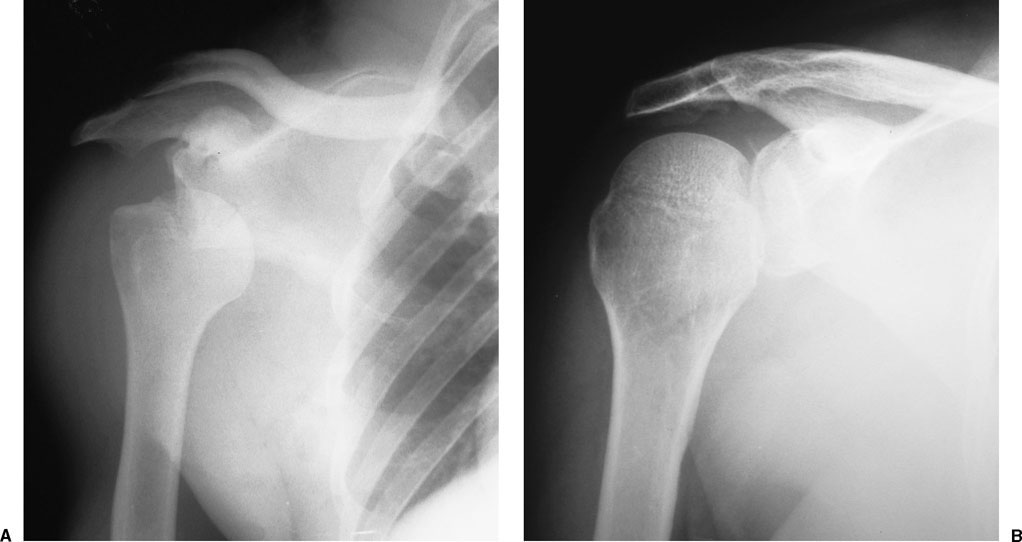
Nevertheless, the possibility of axillary arterial injury should be considered in every fracture of the proximal humerus with severe medial displacement of the shaft. īecause of the rarity of vascular lesions associated with proximal humeral fractures, accompanying arterial lesions can be easily overlooked, especially in fractures not readily associated with arterial injury. Finally, all fractures involving long bones are at higher risk for vascular injuries. Certain skeletal injuries, such as supracondylar humeral fractures, elbow joint dislocation fractures, supracondylar femoral fractures, and posterior knee joint dislocations, are far more often accompanied by vascular lesions, with a frequency of up to 10%. Extremity fractures are accompanied by arterial lesions in 0.9%. However, major vascular injury in association with these fractures is uncommon. Peripheral neurological injury in association with displaced fractures of the proximal humerus is not unusual. The increasing use of endovascular procedures to treat vascular lesions is a very interesting development with several advantages, especially in elderly and multimorbid patients. The specific order in treatment (internal fixation first or vascular repair first) depends on the severity of the accompanying vascular injury. Therefore, we try to emphasize on the importance of thorough and accurate diagnostics, because it is obligatory for early diagnosis and improving the eventual outcome of these injuries. These Injuries are very rare but severe and the accompanying vascular impairment can have great clinical consequences. We present two cases in which displaced proximal humeral fractures are accompanied by vascular injury.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
